In commercial enterprise control and operations, efficient dealing with price ranges and resources is paramount. Whether you're a small startup or a large company, having the right equipment to control your monetary transactions, track expenses, and streamline operations is important for achievement. Accounting software and ERP software programs are commonly used for those functions. While each is crucial for dealing with various elements of a commercial enterprise's finances, they serve wonderful functions and provide different functionalities. In this newsletter, we will delve into the differences between accounting software and ERP software programs, their functions and blessings, and when each might be the right preference for your commercial enterprise.
Understanding Accounting Software
The primary functions of accounting software generally include bookkeeping, invoicing, bills payable and receivable, payroll processing, and economic reporting. It offers companies the sources they need to control budgets, create reviews for compliance, and accurately file and tune financial transactions to make informed choices.
Key Features of Accounting Software:
-
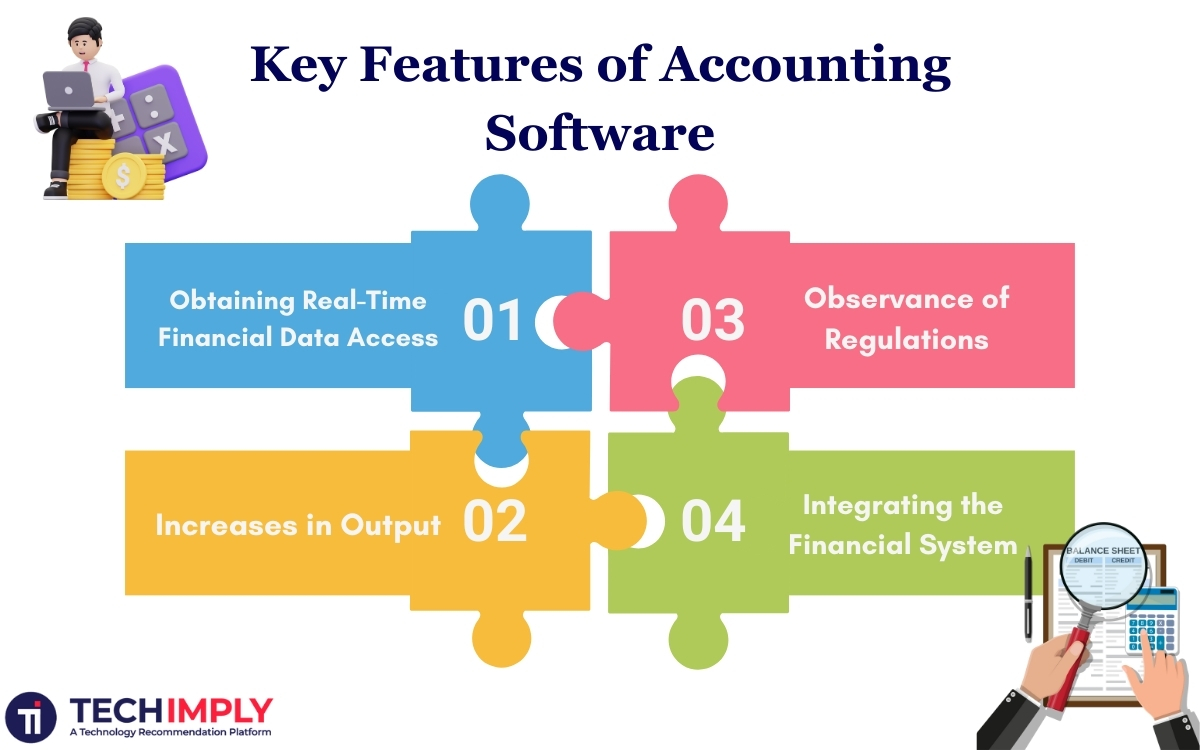
Obtaining Real-Time Financial Data Access: Obtaining up-to-date financial data is crucial in the current hectic commercial landscape. With current information on expenses, profitability, and cash flow, decision-makers can act quickly and decisively, setting their companies up for improved financial management and strategic direction.
-
Increases in Output: Businesses may increase their productivity substantially by using automated solutions for labour-intensive financial operations, including account reconciliation, payroll processing, and invoice production. The time and labour that may be used for strategic planning and corporate growth projects are freed up by this automation.
-
Observance of Regulations: Any firm must stay current on the most recent banking rules and tax laws. Automated financial systems are essential since they help avoid costly fines and ensure that all company activities stay within legal bounds.
-
Integrating the Financial System: The execution of transactions is made simpler by the close integration of banking services and financial systems. Transparency and efficiency in financial operations are ensured by this interconnectedness, which speeds up the reconciliation process and keeps an accurate and accountable record of every economic activity.
Exploring ERP Software
The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software program is going beyond the scope of accounting software, integrating diverse business functions and methods into an unmarried gadget. In addition to accounting and finance, ERP software normally includes modules for inventory management, supply chain control, human resources, client relationship control, and more. The purpose of ERP is to centralize facts and streamline workflows across an entire organization, providing real-time visibility and improving choice-making.
Key Features of ERP Software:
-
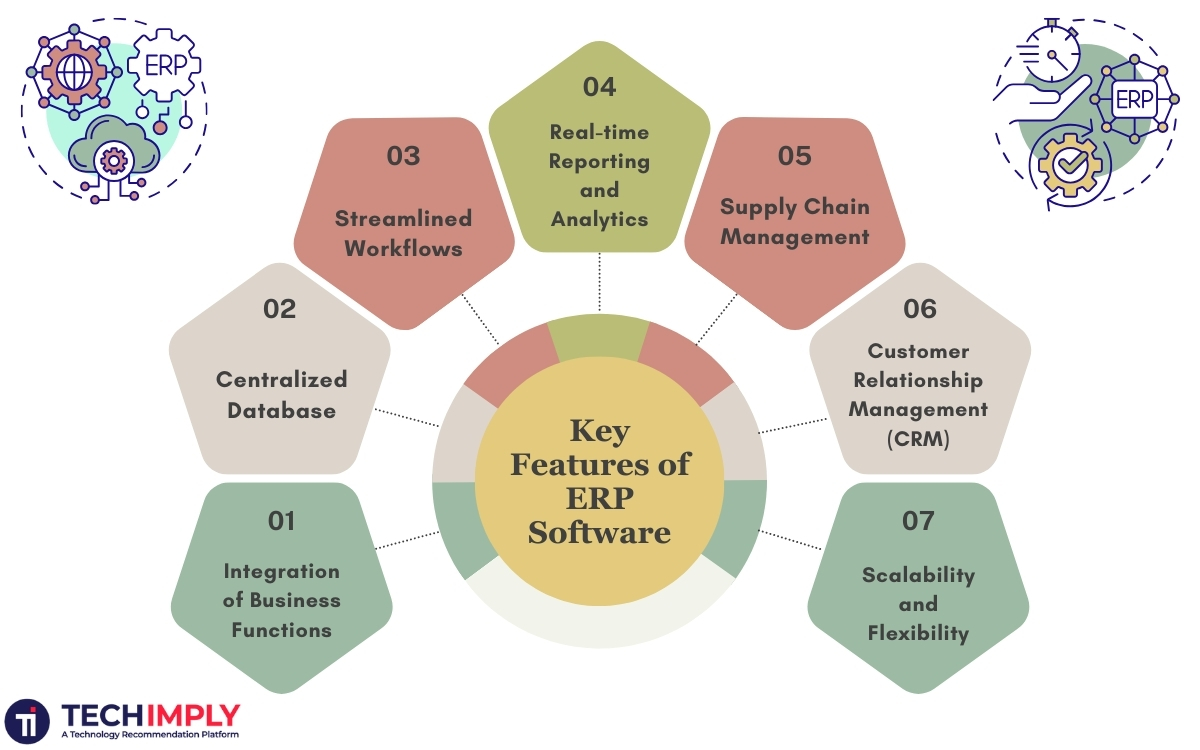
Integration of Business Functions: The ERP software program integrates center enterprise functions like finance, accounting, income, inventory, procurement, manufacturing, and human property into an unmarried platform. This integration gets rid of silos and lets in seamless facts to go along with the float amongst departments.
-
Centralized Database: ERP systems preserve a centralized database that stores all applicable facts, permitting customers access to correct and updated records throughout the agency. This centralized technique improves factual consistency and decreases redundancy.
-
Streamlined Workflows: The ERP software application standardizes and automates company strategies to raise efficiency and productivity. Workflows, which include order processing, inventory manipulation, and procurement, may be optimized to reduce manual intervention and mistakes.
-
Real-time Reporting and Analytics: ERP structures offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing clients to generate custom critiques, dashboards, and KPIs in actual time. This visibility into key metrics allows for informed selection-making and strategic-making plans.
-
Supply Chain Management: ERP software optimizes the chain by handling inventory degrees, tracking shipments, forecasting demand, and coordinating with suppliers and vendors. This guarantees well-timed delivery of goods and decreases expenses.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Many ERP structures encompass CRM capability to manage purchaser interactions, income pipelines, advertising campaigns, and customer support. This method allows companies to provide higher client reviews and pressure an income boom.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: The ERP software program is designed to scale with the desires of the commercial enterprise, whether it is expanding to new markets, including new product traces, or accommodating a boom in transaction volumes. ERP systems are also often configurable to adapt to precise enterprise and regulatory requirements.
Key Differences Between Accounting Software And ERP Software
-
Scope and Integration: Accounting software generally focuses on economic control obligations, including bookkeeping, invoicing, and reporting. In contrast, ERP software integrates multiple business functions, such as finance software, stock software, delivery chain software, HR software, and CRM software.
-
Depth of Functionality: While the accounting software program excels at central financial functions, the ERP software program offers a broader range of functions and deeper capability across numerous business tactics. ERP systems are designed to assist complex operations and provide end-to-end visibility.
-
Scalability: ERP software is generally more scalable than accounting software programs, capable of meeting the wishes of growing organizations' living requirements. As agencies amplify, ERP structures can accommodate extended transaction volumes, customers, and enterprise complexities.
-
CustomizationCustomization: ERP software frequently allows for more customization to meet particular business needs and enterprise requirements. Accounting software may provide some customization, but it usually requires more flexibility.
-
Cost: ERP software programs are more expensive than accounting software programs due to their comprehensive capabilities and broader scope. The value of ERP implementation may also encompass licensing fees, implementation offerings, training, and ongoing upkeep.
-
User Experience: Accounting software programs are usually more person-friendly and easier to navigate because they specialize in monetary tasks. ERP software programs can also have a steeper getting-to-know curve due to their tremendous capability and integration throughout multiple modules.
Choosing The Right Solution For Your Business
When identifying between accounting software and ERP software, don't forget the following factors:

-
Business Size and Complexity: Small agencies with truthful economic desires may also find accounting software sufficient. However, medium- to large-scale organizations with complex operations and more than one department may benefit more from the complete abilities of ERP software programs.
-
Budget and Resources: Evaluate your budget and assets available for software implementation, training, and ongoing guidance. While accounting software programs can be extra cost-effective in advance, ERP software programs offer long-term scalability and ROI for growing corporations.
-
Future Growth and Expansion Plans: Consider your commercial enterprise's boom trajectory and expansion plans. If you expect scaling operations or getting into new markets, investing in ERP software early can offer a basis for future achievement.
-
Industry Requirements: Certain industries have particular regulatory compliance requirements or precise operational wishes. Choose a software program solution that aligns with your enterprise standards and might address enterprise-specific demanding situations.
-
User Needs and Preferences: Involve key stakeholders and quit-users in the software choice technique to ensure the selected solution meets their needs and alternatives. Consider factors that include usability, training requirements, and support options.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: If your enterprise already uses specialized or legacy systems for certain functions, remember how properly the accounting software or ERP device integrates with those existing systems. Seamless integration can streamline operations and reduce data drift.
Conclusion
While accounting software and ERP software programs play vital roles in coping with a business's finances and operations, they serve distinct purposes and offer awesome features. Accounting software programs are right for dealing with middle monetary obligations, including bookkeeping, invoicing, and reporting, even as ERP software programs afford a complete answer that integrates numerous commercial enterprise functions throughout a corporation. When deciding between accounting software and ERP software, remember business length, complexity, budget, increased plans, enterprise requirements, and personal wishes. Ultimately, deciding on the right software program solution can streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and power business success.






